food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome symptoms
When someone says they have a food allergy most people think of symptoms like anaphylaxis or hives or an itchy swollen mouth. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy with potential dehydration secondary to vomiting.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
In about 20 percent of cases the child will experience.
. Vomiting is often followed by a paleness to the skin. Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE mediated food allergy characterized by delayed vomiting in infants that was first described in the 1970s.
What are acute FPIES symptoms. It is caused by an allergic reaction to one or more ingested foods which results in inflammation of the small and large intestine. FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is being increasingly recognized.
In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an adverse food reaction involving the immune system that mainly affects infants and young children. Unlike most food allergies that produce immediate reactions such as hives swelling and respiratory symptoms FPIES reactions are delayed and usually begin about two hours after ingestion of the trigger food.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. Severe vomiting Diarrhea sometimes bloody Weight loss Dehydration Lack of energy Failure to thrive. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that manifests with projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypothermia hypotension and metabolic derangements.
Symptoms of profuse vomiting and sometimes diarrhoea most commonly occur two to four. 3 Diagnosis of FPIES is difficult. Acute FPIES reactions include.
Pathophysiology of FPIES has not yet been clearly defined and needs further characterization. Symptoms can be severe and can potentially cause acute dehydration andor hypovolemic shock. Very severe symptoms can occur ranging from 5 to 24 of cases as intractable protracted vomiting lethargy pallor hypotension dehydration and hypothermia with temperature less than 36 6891113.
Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. FPIES manifests usually in infants as profuse repetitive emesis onset one to three hours after ingestion and diarrhea onset 510 hours that may be accompanied by lethargy. If often happens when starting the first formulas or solid foods.
The syndrome is caused by cells in your childs immune system. We aimed at describing the characteristics of a French population of children with FPIES and define risk factors for failure. FPIES is caused by an allergic reaction to a food which causes inflammation of the small and large intestine.
It typically causes vomiting and bloody diarrhea after consumption of certain foods the trigger foods arent the same for everyone. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food protein. You may notice that a couple of hours after your baby eats they vomit over and over and then get diarrhea.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES Oral Allergy Syndrome OASPollen Food Syndrome PFS. Those dont happen with FPIES and the mechanism in the body that causes FPIES reactions is different from other food allergy disorders. An acute form and a chronic form.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. Such a presentation is often misdiagnosed as. 4 FPIES is most commonly caused by CM and soy.
INTRODUCTION Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition that occurs in infants and young children although it can rarely affect older children or adults as well. Affected infants show gastrointestinal symptoms few hours after ingestion of the incriminating food.
Additional symptoms include pallor lethargy and abdominal swelling distension. FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea.
Each child is different but the most common symptoms of FPIES involve the. 3 The respiratory and skin manifestations are absent in FPIES reactions. FPIES presents in two different forms.
RD on optimizing nutrition in children with. Breast milk doesnt usually cause an FPIES reaction even if the mother has eaten a trigger food. These symptoms can lead to severe lethargy change in body temperature and blood pressure.
What Is Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children. The most common triggers for an episode are milk soy and rice but the disorder has been associated with a wide range of food proteins.
An often underdiagnosed and misdiagnosed condition FPIES was not associated with its own diagnostic code until 2015. Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion Diarrhea that begins after vomiting Dehydration Severe lethargy Changes in. Differences exist regarding culprit foods and age of tolerance depending on the country of origin.
1 2 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food. 59 Symptoms may start in the newborn period or up to one year of. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an unusual type of food allergy.
That makes FPIES hard to test for. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an under-recognized and frequently misdiagnosed non-IgE mediated food allergy syndrome.
It is much less common than IgE-mediated food allergy and usually only occurs in babies and young children. It is a free app intended to help patients and parents understand whether specific symptoms may be caused by a food allergy and whether further advice from an allergist is recommended.

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
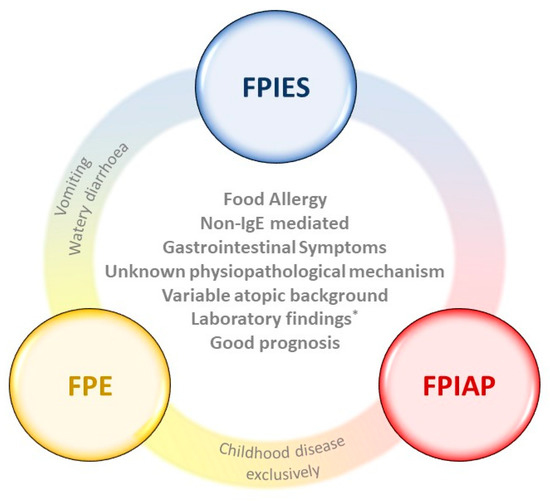
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
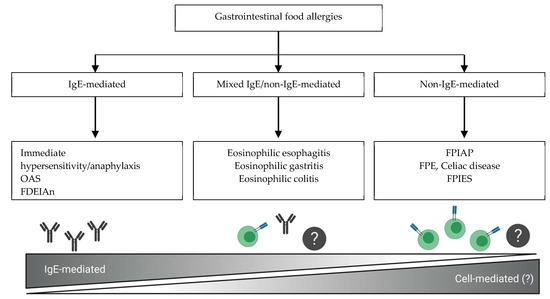
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Pdf Gastrointestinal Food Allergy In Infants Semantic Scholar

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome As A Cause For Infant Hypotension The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Comparison Between Acute And Chronic Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

References In Immunopathophysiology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology